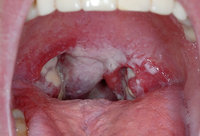
 Group A Beta Hemolytic Streptococcal Pyogenes (GABHS) is a common gram positive bacteria that routinely occupies the upper aero digestive tract of humans and canines. It is estimated that at any given time, up to 10% of the population will be carrying strep around in their pharynges. Perhaps up to 20% of pediatric patients. The difference between colonization and infection (detrimental colinization) is really adverse symptoms. It is felt that it is unnecessary to treat assymptomatic carriers unless there is ARF in the community, a family history of ARF, documented family history of a symptomatic family member, or other related commorbidities.
Group A Beta Hemolytic Streptococcal Pyogenes (GABHS) is a common gram positive bacteria that routinely occupies the upper aero digestive tract of humans and canines. It is estimated that at any given time, up to 10% of the population will be carrying strep around in their pharynges. Perhaps up to 20% of pediatric patients. The difference between colonization and infection (detrimental colinization) is really adverse symptoms. It is felt that it is unnecessary to treat assymptomatic carriers unless there is ARF in the community, a family history of ARF, documented family history of a symptomatic family member, or other related commorbidities.
Most experts agree that a rapid strep test is diagnostic. Follow up cultures for negative studies may be appropriate in younger patients. Cultures are never indicated under the age of 3 as they have not had enough antigenic exposure to develope Rheumatic Heart Disease.
GABHS has a number of known problematic sequelae that are the primary reason we look for it. Although rare, ARF (Acute Rhematic Fever) or Rheumatic Heart Disease is our primary concern. It is a sterile Type II autoimmune attack on the heart valves, myocardium, and joints resulting from the protracted high anti strep circulating antibodies. It is my understanding that if you treat Strep within 9 days you avoid this possibility. Apparently you need to treat about 40,000 cases of strep throat to avoid one such case. With the incidence of a severe allergic reaction to PCN being 1/12,000 so clinical judgement is paramount. The most winning strategy is to just use the “rapid test” as the decision maker. Using this strategy, in the US, we could prevent 85 cases of rheumatic heart disease annually at the cost of $727,000 per case prevented. You are actually more likely to contract Lemeirre’s Syndrome from Fusobacterium with a GABHS infection than Rheumatic Heart Disease.
Other adverse sequalae to strep infections include: Post Streptococcal Glomerular Nephritis (a type III reaction more common after Impetigo), PANDAS (acute childhood OCD), Scarlet Fever, and Toxic Shock Syndrome. It is not clear weather or not early treatment is preventive with this list of pathologies.
It is uncertain if the family dog can act as a reservoir or not. However, there have apparently been case reports, and treating the dog has been suggested by some.
The “over use” of Penicillin like antibiotics can eradicate the normal flora, leaving only the penicillinase producers. This can lead to what seem like fairly resistant cases that fail penicillin repeatedly. If they and family members are asymptomatic, there is no reason to treat. If the decision is to treat (ASO titers can help with that decision), then Cleocin or Ceftibutin can be considered. (Cleocin 20 mg/kg/day divided TID for 10 days). In reality antibiotics have no proven benefit for the treatment of any pharyngitis other than GABHS, Ghonorrhea, or Diptheria.
Another consideration is to wash family toothbrushes in top drawer of dish washer on day 1, 5, and 10 of treatment.